In PET and SPECT, getting more sensitive and working smarter
June 19, 2018
by Lisa Chamoff, Contributing Reporter
Manufacturers in the nuclear imaging space are continuing to innovate in the PET and SPECT markets, increasing the sensitivity of scanners in order to improve diagnosis and treatment, and lower the radiation dose, for patients with cancer and cardiovascular disease, along with other health issues.
At the same time, software companies are looking to help clinicians work smarter with the technology they already have.
Here’s a guide to what’s new to the market for several manufacturers and software companies.
GE Healthcare
GE recently released a five-ring version of its Discovery MI PET/CT system, which has a 25-centimeter field of view. This is in addition to the three- and four-ring Discovery MI systems, which offer a 15-centimeter field of view and a 20-centimeter field of view respectively.
The increased field of view allows for much faster scan times and less injected dose, said Sergio Calvo, GE Healthcare's general manager for PET. The system reduces the acquisition by three times, so a scan that would take 30 minutes could now take 10 minutes.
The system also has GE’s advanced reconstruction algorithms that Calvo said creates an image that is “virtually free of motion artifacts.”
“All of these technologies working in harmony in this system creates the best PET/CT scanner we have ever made,” Calvo said.
The more advanced scanners can also help academic facilities investigate new tracers, particularly for prostate cancer, an area of research where there is a lot of growth and momentum.
“If you have a high-sensitive system, you will be able to image highly specific and low-uptake tracers with great image quality, something that conventional scanners could not do,” Calvo said.
While the big commercial release of the new Discovery MI will take place later this month at SNMMI, the company did its first installations a few months ago at facilities including the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Massachusetts General Hospital and MD Anderson in Houston, Texas.
In the SPECT space, GE is planning to introduce new products at SNMMI. The company will also showcase the second generation of its Discovery NM/CT 670 CZT, which has higher sensitivity, allowing for a shorter acquisition time.
“A whole-body bone scan takes half the time, from 10 minutes to five minutes [on the second-generation Discovery NM/CT 670 CZT],” said Nathan Hermony, GE’s general manager for nuclear medicine.
Hermony said while other manufacturers have been investing less in SPECT, GE has decided to continue moving forward in the space.
“Each modality, SPECT and PET, has many different procedures and they complement each other,” Hermony said of PET and SPECT. “This is clearly something we believe in. We see both modalities growing. We don’t see one at the expense of the other.”
Hermes Medical Solutions
The company received FDA approval for its SUV SPECT software in 2014. The software allows facilities to measure the standardized uptake value (SUV), or the concentration of radioactivity, of a lesion during the reconstruction of the SPECT images.
This is essential for the new revolution in molecular imaging, dosimetry and theranostics, said Francois Hebert, director of sales for Canada and business development for North America for Hermes Medical Solutions.
“New personalized and precise treatments will, in some cases, replace radiotherapy, being more targeted and accurate in the fight against cancer,” Hebert said.
Hebert said most facilities are doing visual assessments of how cancer is responding to treatment, comparing them visually to a baseline exam.
“If it wasn’t acquired on the same type of scanner, there was no way to compare them,” Hebert said.
SUV SPECT is vendor neutral, allowing facilities with SPECT systems from multiple vendors to use the software platform. Larger OEM manufacturers have similar technology, but only compatible with their own systems.
The company also offers a similar software product in Canada and Europe for nuclear cardiology that can identify issues, such as balanced triple-vessel disease, which may be missed with a visual assessment during a stress test.
“The only other way to tell that is to send the patient to the cath lab for an invasive procedure,” Hebert said. “Anything that requires a follow up is a good candidate for that technique.”
Mirada Medical
Mirada Medical’s newest diagnostic software product, XD Nuclear Medicine, offers nuclear medicine and radiology departments online workflows that can be customized and integrated into a PACS system.
Currently, nuclear medicine studies have to be processed on dedicated workstations attached to specific nuclear medicine cameras. But with XD Nuclear Medicine, “nuclear medicine studies can be both processed and read via the PACS, reducing the need for dedicated workstations,” said Sarah Bond, vice president of product management for Mirada Medical.
“It becomes a much more accessible way of providing comprehensive Nuclear Medicine software through the PACS or hospital enterprise,” Bond said. “It’s also cheaper from an IT maintenance perspective because it consolidates how hospitals manage their nuclear medicine imaging.”
With Mirada software, staff can save regions of interest, TACs and statistics and then come back to the same place later, regardless of physical location within the hospital, Bond said.
The software works with nuclear medicine scanners from any manufacturer, freeing staff from being locked into using specific workstations to perform tasks, and departments from expensive OEM service contracts, Bond said.
Philips Healthcare
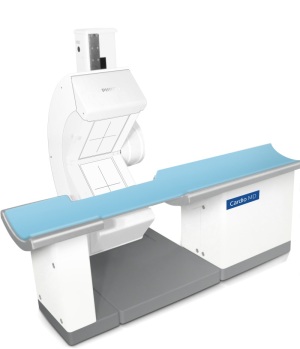
In September 2017, Philips released CardioMD IV, a small SPECT system for cardiac imaging.
The system, which is currently only available only in U.S., uses the company’s advanced Astonish reconstruction and cardiac quantification software to improve diagnostic confidence and workflow for cardiac imaging.
“Recognizing molecular imaging's potential to transform healthcare, CardioMD IV is tailored to address the most pressing challenges in cardiac imaging today,” said Tom Neufelder, head of CT and advanced molecular imaging for Philips.
The dedicated cardiac SPECT solution has a small footprint, to fit in most existing camera rooms without requiring costly renovations. The design allows for greater positioning flexibility, and the Astonish reconstruction improves workflow efficiency without sacrificing image quality.
CardioMD IV can be combined with IntelliSpace Portal, Philips' advanced visualization and analysis platform, to provide enterprise-wide access to the latest cardiac SPECT quantification, review and reporting applications while enabling effective collaboration among cardiologists and referring physicians, according to Neufelder.
"Our aim is to advance molecular imaging in all disease areas and provide dependable imaging solutions to enhance diagnostic confidence and patient care at lower costs," Neufelder said.
Siemens Healthineers
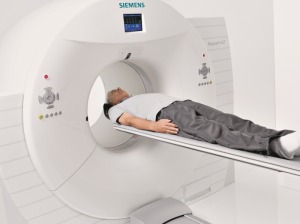
The company recently released a new set of features for its Biograph mCT family of PET/CT systems. One of the features is OncoFreeze, a technology for respiratory gaiting that allows for virtually motion-free images without increasing scan time.
“Before, you took a portion of the breathing cycle, extending the scan time” said Wendy Winkle-Lawless, director of marketing for molecular imaging at Siemens Healthineers. “Now we’ve found a way to take every portion of the breathing cycle, overlap it and correct for that motion. Before you would have to at least double your time or do a second scan over that area of the body. Most would add 10 to 15 minutes to the scan slot. Now, with OncoFreeze, you can do it in the same scan slot as if a patient wasn’t being gated.”
The technology is particularly helpful for scanning lung cancer patients.
“Having virtually motion free images could make a big difference in how you diagnose or stage patients if you can see tumors more clearly,” Winkle-Lawless said.
There is also CardioFreeze for cardiac gating, which corrects for both motion of the heart caused by breathing and the beating of the heart.
“It allows you to get a more precise gate,” Winkle-Lawless said.
Both features are also intended to increase patient comfort and improve outcomes, Winkle-Lawless said.
The new features also include QualityGuard, which allows the scanner to calibrate itself daily, overnight, without the need for a radioactive phantom. A phantom is only used quarterly for full calibration.
Winkle-Lawless said QualityGuard should save customers 120 hours per year and will help reduce risks to workers when lifting the phantom, while exposing them to less radiation.
“Now you can come in in the morning and immediately start scanning patients,” Winkle-Lawless said. “You could add an extra scan slot per day.”
Recently, Siemens received FDA clearance to use a technology called FlowMotion Multiparametric PET Suite on its PET systems. During imaging, the patient is scanned multiple times, instead of just once, which provides important information about the uptake of a tracer.
“It allows you to evaluate metabolic activity in the tissue over time,” Winkle-Lawless said.
At the same time, software companies are looking to help clinicians work smarter with the technology they already have.
Here’s a guide to what’s new to the market for several manufacturers and software companies.
GE Healthcare
GE recently released a five-ring version of its Discovery MI PET/CT system, which has a 25-centimeter field of view. This is in addition to the three- and four-ring Discovery MI systems, which offer a 15-centimeter field of view and a 20-centimeter field of view respectively.
The increased field of view allows for much faster scan times and less injected dose, said Sergio Calvo, GE Healthcare's general manager for PET. The system reduces the acquisition by three times, so a scan that would take 30 minutes could now take 10 minutes.
The system also has GE’s advanced reconstruction algorithms that Calvo said creates an image that is “virtually free of motion artifacts.”
“All of these technologies working in harmony in this system creates the best PET/CT scanner we have ever made,” Calvo said.
The more advanced scanners can also help academic facilities investigate new tracers, particularly for prostate cancer, an area of research where there is a lot of growth and momentum.
“If you have a high-sensitive system, you will be able to image highly specific and low-uptake tracers with great image quality, something that conventional scanners could not do,” Calvo said.
While the big commercial release of the new Discovery MI will take place later this month at SNMMI, the company did its first installations a few months ago at facilities including the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Massachusetts General Hospital and MD Anderson in Houston, Texas.
In the SPECT space, GE is planning to introduce new products at SNMMI. The company will also showcase the second generation of its Discovery NM/CT 670 CZT, which has higher sensitivity, allowing for a shorter acquisition time.
“A whole-body bone scan takes half the time, from 10 minutes to five minutes [on the second-generation Discovery NM/CT 670 CZT],” said Nathan Hermony, GE’s general manager for nuclear medicine.
Hermony said while other manufacturers have been investing less in SPECT, GE has decided to continue moving forward in the space.
“Each modality, SPECT and PET, has many different procedures and they complement each other,” Hermony said of PET and SPECT. “This is clearly something we believe in. We see both modalities growing. We don’t see one at the expense of the other.”
Hermes Medical Solutions
The company received FDA approval for its SUV SPECT software in 2014. The software allows facilities to measure the standardized uptake value (SUV), or the concentration of radioactivity, of a lesion during the reconstruction of the SPECT images.
This is essential for the new revolution in molecular imaging, dosimetry and theranostics, said Francois Hebert, director of sales for Canada and business development for North America for Hermes Medical Solutions.
“New personalized and precise treatments will, in some cases, replace radiotherapy, being more targeted and accurate in the fight against cancer,” Hebert said.
Hebert said most facilities are doing visual assessments of how cancer is responding to treatment, comparing them visually to a baseline exam.
“If it wasn’t acquired on the same type of scanner, there was no way to compare them,” Hebert said.
SUV SPECT is vendor neutral, allowing facilities with SPECT systems from multiple vendors to use the software platform. Larger OEM manufacturers have similar technology, but only compatible with their own systems.
The company also offers a similar software product in Canada and Europe for nuclear cardiology that can identify issues, such as balanced triple-vessel disease, which may be missed with a visual assessment during a stress test.
“The only other way to tell that is to send the patient to the cath lab for an invasive procedure,” Hebert said. “Anything that requires a follow up is a good candidate for that technique.”
Mirada Medical
Mirada Medical’s newest diagnostic software product, XD Nuclear Medicine, offers nuclear medicine and radiology departments online workflows that can be customized and integrated into a PACS system.
Currently, nuclear medicine studies have to be processed on dedicated workstations attached to specific nuclear medicine cameras. But with XD Nuclear Medicine, “nuclear medicine studies can be both processed and read via the PACS, reducing the need for dedicated workstations,” said Sarah Bond, vice president of product management for Mirada Medical.
“It becomes a much more accessible way of providing comprehensive Nuclear Medicine software through the PACS or hospital enterprise,” Bond said. “It’s also cheaper from an IT maintenance perspective because it consolidates how hospitals manage their nuclear medicine imaging.”
With Mirada software, staff can save regions of interest, TACs and statistics and then come back to the same place later, regardless of physical location within the hospital, Bond said.
The software works with nuclear medicine scanners from any manufacturer, freeing staff from being locked into using specific workstations to perform tasks, and departments from expensive OEM service contracts, Bond said.
Philips Healthcare
In September 2017, Philips released CardioMD IV, a small SPECT system for cardiac imaging.
The system, which is currently only available only in U.S., uses the company’s advanced Astonish reconstruction and cardiac quantification software to improve diagnostic confidence and workflow for cardiac imaging.
“Recognizing molecular imaging's potential to transform healthcare, CardioMD IV is tailored to address the most pressing challenges in cardiac imaging today,” said Tom Neufelder, head of CT and advanced molecular imaging for Philips.
The dedicated cardiac SPECT solution has a small footprint, to fit in most existing camera rooms without requiring costly renovations. The design allows for greater positioning flexibility, and the Astonish reconstruction improves workflow efficiency without sacrificing image quality.
CardioMD IV can be combined with IntelliSpace Portal, Philips' advanced visualization and analysis platform, to provide enterprise-wide access to the latest cardiac SPECT quantification, review and reporting applications while enabling effective collaboration among cardiologists and referring physicians, according to Neufelder.
"Our aim is to advance molecular imaging in all disease areas and provide dependable imaging solutions to enhance diagnostic confidence and patient care at lower costs," Neufelder said.
Siemens Healthineers
The company recently released a new set of features for its Biograph mCT family of PET/CT systems. One of the features is OncoFreeze, a technology for respiratory gaiting that allows for virtually motion-free images without increasing scan time.
“Before, you took a portion of the breathing cycle, extending the scan time” said Wendy Winkle-Lawless, director of marketing for molecular imaging at Siemens Healthineers. “Now we’ve found a way to take every portion of the breathing cycle, overlap it and correct for that motion. Before you would have to at least double your time or do a second scan over that area of the body. Most would add 10 to 15 minutes to the scan slot. Now, with OncoFreeze, you can do it in the same scan slot as if a patient wasn’t being gated.”
The technology is particularly helpful for scanning lung cancer patients.
“Having virtually motion free images could make a big difference in how you diagnose or stage patients if you can see tumors more clearly,” Winkle-Lawless said.
There is also CardioFreeze for cardiac gating, which corrects for both motion of the heart caused by breathing and the beating of the heart.
“It allows you to get a more precise gate,” Winkle-Lawless said.
Both features are also intended to increase patient comfort and improve outcomes, Winkle-Lawless said.
The new features also include QualityGuard, which allows the scanner to calibrate itself daily, overnight, without the need for a radioactive phantom. A phantom is only used quarterly for full calibration.
Winkle-Lawless said QualityGuard should save customers 120 hours per year and will help reduce risks to workers when lifting the phantom, while exposing them to less radiation.
“Now you can come in in the morning and immediately start scanning patients,” Winkle-Lawless said. “You could add an extra scan slot per day.”
Recently, Siemens received FDA clearance to use a technology called FlowMotion Multiparametric PET Suite on its PET systems. During imaging, the patient is scanned multiple times, instead of just once, which provides important information about the uptake of a tracer.
“It allows you to evaluate metabolic activity in the tissue over time,” Winkle-Lawless said.