by
John R. Fischer, Senior Reporter | October 15, 2020
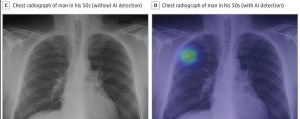
Lunit INSIGHT CXR showed higher specificity in detecting malignant lung cancers than radiologists
An AI algorithm designed by Lunit has shown potential for improving lung cancer detection on chest radiographs.
Teaming up with researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital, the AI startup found that its solution, Lunit INSIGHT CXR, showed higher sensitivity than radiologists in finding malignant pulmonary nodules on chest X-rays derived from participants in the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST).
"It is a meaningful study to show Lunit INSIGHT CXR can be utilized to diagnose cancer-related nodules and detect lung cancer in earlier stages,” said Brandon Suh, CEO of Lunit, in a statement.




Ad Statistics
Times Displayed: 30380
Times Visited: 760 Stay up to date with the latest training to fix, troubleshoot, and maintain your critical care devices. GE HealthCare offers multiple training formats to empower teams and expand knowledge, saving you time and money
Radiologists tested the product on 5,485 chest radiographs. The AI algorithm showed 94% sensitivity in locating malignant pulmonary nodules — higher than that of NLST radiologists — as well as 83% specificity. The results imply that it could potentially be used as a second reader to help detect lung cancer.
They also signify the potential use of chest radiographs in place of CT. Many medical societies recommended low-dose CT for lung cancer screening due to the projectional nature of radiography making the detection of chest radiographs a challenge for radiologists.
"Compared with chest radiography, CT is less accessible and more expensive, exposing patients to a higher dose of radiation,” said Subba Digumarthy, the senior author of the study and an attending thoracic radiologist at MGH. “This study shows that AI can provide diagnostic value to more patients by supplementing the shortcomings and maintaining the advantages of X-ray diagnosis."
Lunit INSIGHT CXR was
showcased in November 2019 at the annual Radiological Society of North America meeting in Chicago and
gained CE mark status the same month.
The findings were published in
JAMA Network Open.

