by
John R. Fischer, Senior Reporter | March 29, 2022
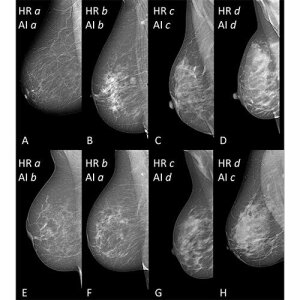
An AI tool called TRACE4BDensity may accurately classify breast density on mammograms.
Researchers in Italy have developed a new AI tool capable of accurately and consistently classifying breast density on mammograms.
The solution is called TRACE4BDensity and is not affected by limitations such as different assessments made by two or more radiologists, as well as variations in multiple examinations made by the same person. Based on deep learning with convolutional neural networks, it instead can discern subtle patterns in images beyond the capabilities of the human eye.
Women with extremely dense breasts are at a three-to-six times higher risk of developing breast cancer than women with almost entirely fatty breasts and a two-fold higher risk than the average woman. Mammography is less sensitive in being able to detect cancer in these patients, with density masking the presence of tumors.




Ad Statistics
Times Displayed: 44025
Times Visited: 1347 Keep biomedical devices ready to go, so care teams can be ready to care for patients. GE HealthCare’s ReadySee™ helps overcome frustrations due to lack of network and device visibility, manual troubleshooting, and downtime.
Many states have passed laws that require women to be notified of their density following a mammogram so that they can decide with their doctors if supplementary testing is appropriate. And as of February 2019, all U.S. mammography reports nationwide
must include up-to-date information about a woman’s breast tissue density, including if a patient has dense breast tissue and what risks the condition carries.
“The particular value of this tool is the possibility to overcome the suboptimal reproducibility of visual human density classification that limits its practical usability,” said study co-author Dr. Sergio Papa, from the Centro Diagnostico Italiano in Milan, in a statement. “To have a robust tool that proposes the density assignment in a standardized fashion may help a lot in decision-making.”
The tool was trained by seven experienced radiologists and on 760 mammograms they each independently assessed. Three other radiologists used it to assess 384 mammographic images obtained from a different center. TRACE4BDensity was 89% accurate in distinguishing between low density (BI-RADS categories A and B) and high density (categories C and D). The three readers agreed with the tool 90% of the time, and all disagreements were in adjacent BI-RADS categories.
The researchers predict that its value will grow as breast cancer screening continues to become more personalized, with density assessment now considered to be one of the important factors in determining a woman’s risk of developing breast cancer. They plan to conduct additional studies to better understand the tool and what applications it can be used for, especially in countries where regulations on breast density are not active.

